Antibiotics, Prescription Medication
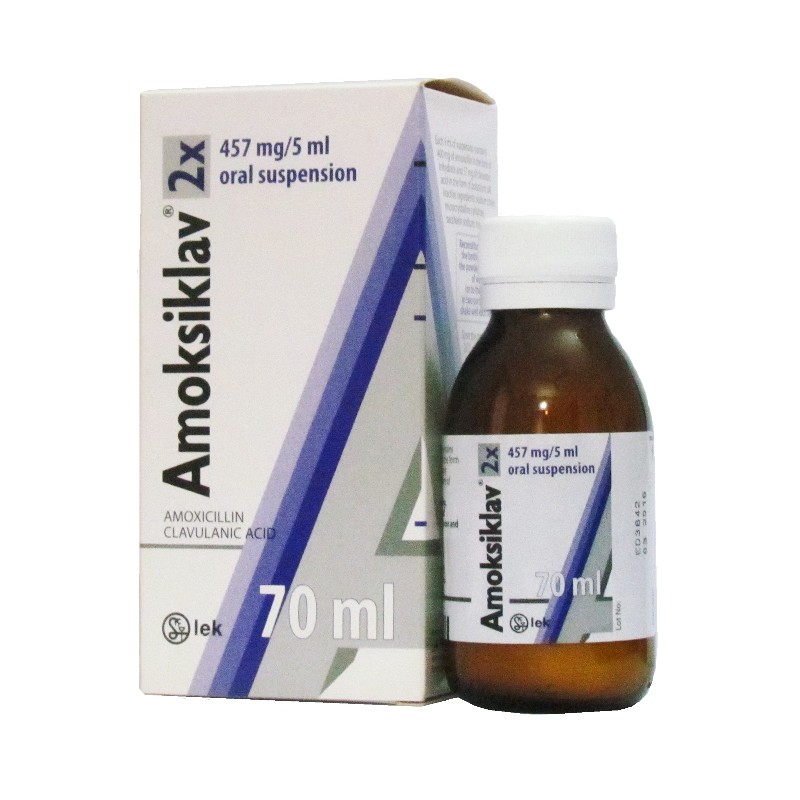
Amoksiklav Suspension
₵ 98.00
-
 Get 10% discount on your next order. Order now to qualify.
Get 10% discount on your next order. Order now to qualify.
-
 Get 20% cashback on apple app store. Use code P056
Get 20% cashback on apple app store. Use code P056
DELIVERY & RETURNS
Free shipping offer on Pilldoctor and get exclusive offers.
Location
-
Door Delivery Fastest delivery to the door for only 2 days. Don't miss exclusive offer.
-
Pickup Station Fastest delivery to the door for only 2 days. Don't miss exclusive offer.
-

Return Policy Fastest delivery to the door for only 2 days. Don't miss exclusive offer.
Description
Each 375-mg tablet (375 mg) contains amoxycillin 250 mg in the form of trihydrate and clavulanic acid 125 mg in the form of potassium salt.
Each teaspoonful (5 mL) of suspension contains amoxycillin 125 mg in the form of trihydrate and clavulanic acid 31.25 mg in the form of potassium salt, respectively.
Action
Pharmacology: Amoksiklav is a combination of amoxycillin and clavulanic acid. Clavulanic acid is produced by the fermentation of Streptomyces clavuligerus. It has a weak antibacterial activity alone, but may prove to act as a potent irreversible β-lactamase inhibitor. With enzyme, it produces stable non-active complexes and protects amoxycillin from degradation.
Pharmacokinetics: Both components of Amoksiklav are well absorbed after oral administration; food has no effect on the degree of absorption.
The pharmacokinetic properties of amoxycillin and clavulanic acid are similar. Peak serum concentrations are achieved approximately 1 hr after ingestion. The biologic half-life of amoxycillin is 78 min and that of clavulanic acid is 60-70 min. In patients with impaired renal function, excretion of Amoksiklav from the body is delayed; it accumulates in the blood proportionately to the degree of renal impairment.
Microbiology: Amoksiklav possesses a broad-spectrum of activity. It is active against ampicillin-susceptible microorganism: Gram-positive cocci (Streptococcus pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, A. viridans, Streptomyces bovis, some strains of Staphylococcus aureus); gram-negative aerobes (Neisseria meningitides, Pasteurela multocida, etc); many anaerobes (anaerobic cocci, Clostridium spp, Bacteroides spp, oropharyngeal strains, Actinomyces israelli, Listeria, Enterococcus), resistant β-lactamase producing bacteria (Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, S. aureus, S. epidermidis, N. gonorrhorae, Bacteroides spp) as well as Escherichia coli, Proteus spp and Klebsiella spp.
Pharmacokinetics: Both components of Amoksiklav are well absorbed after oral administration; food has no effect on the degree of absorption.
The pharmacokinetic properties of amoxycillin and clavulanic acid are similar. Peak serum concentrations are achieved approximately 1 hr after ingestion. The biologic half-life of amoxycillin is 78 min and that of clavulanic acid is 60-70 min. In patients with impaired renal function, excretion of Amoksiklav from the body is delayed; it accumulates in the blood proportionately to the degree of renal impairment.
Microbiology: Amoksiklav possesses a broad-spectrum of activity. It is active against ampicillin-susceptible microorganism: Gram-positive cocci (Streptococcus pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, A. viridans, Streptomyces bovis, some strains of Staphylococcus aureus); gram-negative aerobes (Neisseria meningitides, Pasteurela multocida, etc); many anaerobes (anaerobic cocci, Clostridium spp, Bacteroides spp, oropharyngeal strains, Actinomyces israelli, Listeria, Enterococcus), resistant β-lactamase producing bacteria (Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, S. aureus, S. epidermidis, N. gonorrhorae, Bacteroides spp) as well as Escherichia coli, Proteus spp and Klebsiella spp.
Indications/Uses
Treatment of upper and lower respiratory tract infections (acute and chronic sinusitis, chronic bronchitis, mild lower respiratory tract infections); acute and chronic otitis media; urinary tract infections; gynaecological infections; gonorrhoea (caused by β-lactamase-producing gonococcus); bites of animals or man; skin and soft tissue infections; bone and joint infections; cholecystitis; chancroid; odontogenic infections.
Treatment of mixed infections due to gram-negative and -positive microorganisms and anaerobes: Chronic sinusitis and otitis, cerebral abscess, peritonsillar abscess, mammary abscess, aspiration pneumonia, peritonitis, cholangitis, postoperative intra-abdominal complications, mixed abdominal infections.
Treatment of mixed infections due to gram-negative and -positive microorganisms and anaerobes: Chronic sinusitis and otitis, cerebral abscess, peritonsillar abscess, mammary abscess, aspiration pneumonia, peritonitis, cholangitis, postoperative intra-abdominal complications, mixed abdominal infections.
Dosage/Direction for Use
Adults and Children >40 kg: The usual daily dose is one 375-mg tablet every 8 hrs. Severe Infections: 625 mg every 8 hrs.
The exact children’s doses are based on body weight. Depending Upon Severity of Infection: Children <40 kg: 20-40 mg/kg/day (amoxycillin based), divided into 3 equal doses. Tablets should not be given to children <40 kg.
Usual Dose in Children: Children >7 years: 2 teaspoonfuls (10 mL) of suspension every 8 hrs; 1-7 years: 1 teaspoonful (5 mL) of suspension every 8 hrs; 3 months-1 year: ½ teaspoonful (2.5 mL) suspension every 8 hrs.
Severe Renal Insufficiency (creatinine clearance 10-30 mL/min): The dose should be reduced, or the dosage interval prolonged to 12-18 hrs, respectively and in anuria to ≥48 hrs.
Treatment with Amoksiklav usually lasts for 10 days.
Administration: Reconstitution: Amoksiklav Suspension: Shake the bottle to loosen the powder, add 86 mL of water in 2 portions (or first to 2/3 and then to the mark) and shake well each addition of water.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to penicillin group of antibiotics, infectious mononucleosis, lymphatic leukaemia.
Special Precautions
Amoksiklav should be used with caution in patients with a history of allergic reactions.
In patients with severe liver or renal impairment, the dose should be adequately adjusted or the dosing interval prolonged.
Use in pregnancy & lactation: Safety for use in pregnancy has not been established although animal studies revealed no evidence of teratogenicity.
Both amoxycillin and clavulanic acid are excreted in breast milk, therefore Amoksiklav should not be administered to a nursing mother.
In patients with severe liver or renal impairment, the dose should be adequately adjusted or the dosing interval prolonged.
Use in pregnancy & lactation: Safety for use in pregnancy has not been established although animal studies revealed no evidence of teratogenicity.
Both amoxycillin and clavulanic acid are excreted in breast milk, therefore Amoksiklav should not be administered to a nursing mother.
Use In Pregnancy & Lactation
Use in pregnancy & lactation: Safety for use in pregnancy has not been established although animal studies revealed no evidence of teratogenicity.
Both amoxycillin and clavulanic acid are excreted in breast milk, therefore Amoksiklav should not be administered to a nursing mother.
Both amoxycillin and clavulanic acid are excreted in breast milk, therefore Amoksiklav should not be administered to a nursing mother.
Side Effects
Side effects are generally mild. The most frequently reported are gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea). These reactions can be minimised if Amoksiklav is taken with meals. If a patient develops diarrhoea, the possibility of pseudomembranous colitis needs to be considered.
Skin reactions may occur (pruritus, maculopapular exanthema, rash). If urticaria occurs, treatment should be discontinued.
A rise in hepatic enzymes may rarely occur.
Skin reactions may occur (pruritus, maculopapular exanthema, rash). If urticaria occurs, treatment should be discontinued.
A rise in hepatic enzymes may rarely occur.
Drug Interactions
The concurrent administration of Amoksiklav and methotrexate increases methotrexate toxicity.
Concomitant use with allopurinol appears to increase incidence of exanthema.
Amoksiklav and aminoglycosides used in combination are physically and chemically incompatible.
Laboratory Test Interactions: With Benedict’s reagent it produces false-positive glucose reaction in urine and positive Coombs test.
Concomitant use with allopurinol appears to increase incidence of exanthema.
Amoksiklav and aminoglycosides used in combination are physically and chemically incompatible.
Laboratory Test Interactions: With Benedict’s reagent it produces false-positive glucose reaction in urine and positive Coombs test.
Storage
Store in a dry place, below 25°C.
Reconstituted suspensions and drops must be stored in refrigerator and used within 7 days.
Close the bottle with tablets immediately after using.
Reconstituted suspensions and drops must be stored in refrigerator and used within 7 days.
Close the bottle with tablets immediately after using.
Product Ratings
Highest Ratings
There are no reviews yet.
Rate